11 KiB
Getting Started
This document pertains to Coder-specific implementation of VS Code: code-server. For documentation on how to use VS Code itself, please refer to the official VS Code documentation.
If you get stuck or need help at anytime, file an issue, tweet (@coderhq) or email.
Quickstart Guide
It takes just a few minutes to get your own self-hosted server running. If
you've got a machine running macOS or Linux, you're ready to start the
binary which listens on port 8443 by default.
- Visit the releases page and download the latest release for your operating system.
- Extract the archive and double click the executable to run in the current directory.
- Copy the password that appears in the output.
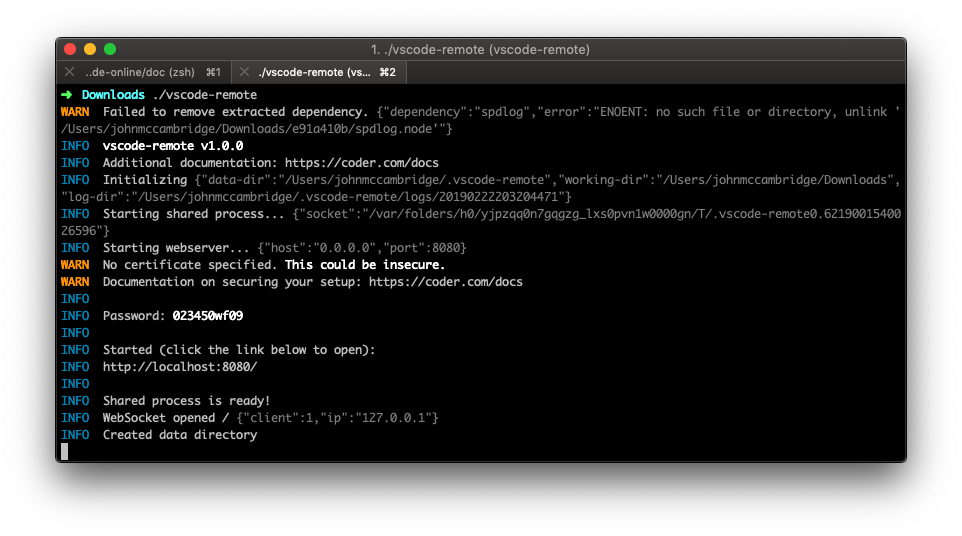
- In your browser navigate to https://localhost:8443. You will be greeted with an SSL warning as code-server uses a self-signed certificate (more on that below). Skip the warning.
- Login using the password from earlier.
Be careful about who you share your password with, as it will grant them full access to your server.
Security Warnings
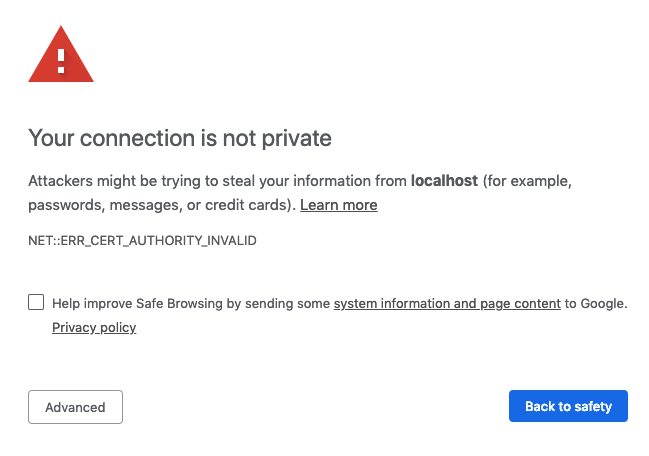
When you visit your code-server instance, you will be greeted with a warning
page similar to the following screenshot. code-server is using a self-signed SSL
certificate for easy setup. In Chrome/Chromium, click Advanced then click
proceed anyway. In Firefox, click Advanced, then Add Exception,
then finally Confirm Security Exception.
code-server Usage
You can bring up code-server usage by using code-server --help. Arguments let
you customize your working directory, host, port, SSL certificates, and more.
Flags can be supplied to code-server like --flag-name value or
--flag-name=value. To supply values with whitespace, use double quotes.
$ code-server --help
Usage: code-server [options]
Run VS Code on a remote server.
Options:
-V, --version output the version number
--cert <value>
--cert-key <value>
-e, --extensions-dir <dir> Override the main default path for user extensions.
--extra-extensions-dir [dir] Path to an extra user extension directory (repeatable). (default: [])
--extra-builtin-extensions-dir [dir] Path to an extra built-in extension directory (repeatable). (default: [])
-d --user-data-dir <dir> Specifies the directory that user data is kept in, useful when running as root.
-h, --host <value> Customize the hostname. (default: "0.0.0.0")
-o, --open Open in the browser on startup.
-p, --port <number> Port to bind on. (default: 8443)
-N, --no-auth Start without requiring authentication.
-H, --allow-http Allow http connections.
--disable-telemetry Disables ALL telemetry.
--socket <value> Listen on a UNIX socket. Host and port will be ignored when set.
--install-extension <value> Install an extension by its ID.
-h, --help output usage information
By default, code-server listens on 0.0.0.0:8443. If you'd like to customize
this, use the --host and --port flags:
code-server --host 127.0.0.1 --port 1234.
You can instruct code-server to automatically open itself in your default
browser by using the -o or --open flag.
Use code-server -d path/to/directory to specify where code-server stores it's
configuration data. You can specify where extensions are installed using the
-e, --extra-extensions-dir and --extra-builtin-extensions-dir flags.
SSL Certificates
To change the certificate code-server uses for HTTPS connections, specify a
certificate with --cert and a private key with --cert-key.
If you're using Let's Encrypt, you should be using the fullchain.pem file as
the certificate and privkey.pem as the private key.
code-server \
--cert /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem \
--cert-key /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem
For more information on security and SSL configuration, please visit the security documentation.
Telemetry
Telemetry can be disabled by using the --disable-telemetry flag or by setting
the DISABLE_TELEMETRY environment variable to true. If telemetry is enabled,
code-server will send the following data along with VS Code's telemetry data:
- Unique machine ID
- CPU core count and model
- Memory information
- Shell information (which shell you use)
- OS release and architecture
Nginx Reverse Proxy
The following site configuration file works with code-server. When starting
code-server, be sure to provide the --allow-http and --trust-proxy flags so
Nginx can connect to code-server properly.
Some of these directives require a version of Nginx greater than or equal to
1.13.0, which might not be available in your distro's repositories. Check out
Nginx's documentation for more information on how to install
the latest version of Nginx from the official repository.
# HTTP configuration
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name code.example.com code.example.org;
# If you're using CloudFlare, uncomment the following line.
# real_ip_header CF-Connecting-IP;
# Other security options.
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8443/;
proxy_set_header Accept-Encoding gzip;
proxy_set_header Connection upgrade;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
# HTTPS configuration. Scores an A on SSL Labs' SSL Server Test.
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name code.example.com code.example.org;
# If you're using CloudFlare, uncomment the following line.
# real_ip_header CF-Connecting-IP;
# SSL certificate and key.
ssl_certificate /path/to/cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /path/to/cert-key.pem;
# Strong TLS configuration. Originally taken from https://cipherli.st/.
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/dhparam.pem; # openssl dhparam -out /etc/nginx/dhparam.pem 4096
ssl_ciphers EECDH+AESGCM:EDH+AESGCM;
ssl_ecdh_curve secp384r1;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 valid=300s;
resolver_timeout 5s;
# Other security options.
# add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubDomains; preload";
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8443/;
proxy_set_header Accept-Encoding gzip;
proxy_set_header Connection upgrade;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
Make sure to set the proxy_pass directive to the actual address of your
code-server instance and the server_name directive to the hostname/s of your
website. If you're using an SSL certificate, make sure to change the
ssl_certificate and ssl_certificate_key directives. If not, remove the HTTPS
server block entirely.
Apache Reverse Proxy
The following virtual host configuration file works with code-server. When
starting code-server, be sure to provide the --allow-http and --trust-proxy
flags so Apache can connect to code-server properly.
Some of these directives require a version of Apache greater than or equal to
2.4.0, which might not be available in your distro's repositories. You will
also need to enable the following modules: rewrite, proxy, proxy_http,
proxy_wstunnel, ssl, and socache_shmcb.
# HTTP configuration.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName code.example.com
# If you're using CloudFlare, uncomment the following line.
# RemoteIPHeader CF-Connecting-IP;
# Other security options.
Header always set X-Frame-Options DENY
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options nosniff
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Upgrade} websocket [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Connection} upgrade [NC]
RewriteRule .* "ws://localhost:8443%{REQUEST_URI}" [P]
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto https
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Port 443
ProxyRequests off
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8443/ nocanon
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8443/
</VirtualHost>
# HTTPS configuration. Scores an A on SSL Labs' SSL Server Test.
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
SSLStaplingCache shmcb:/tmp/stapling_cache(150000)
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName code.example.com
# If you're using CloudFlare, uncomment the following line.
# RemoteIPHeader CF-Connecting-IP;
# SSL certificate and key.
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /path/to/cert.pem
SSLCertifcateKeyFile /path/to/cert-key.pem
SSLCertificateChainFile /path/to/chain.pem
# Strong TLS configuration. Originally taken from https://cipherli.st/.
SSLCipherSuite EECDH+AESGCM:EDH+AESGCM
SSLProtocol -all +TLSv1.2
SSLHonorCipherOrder On
SSLCompression off
SSLUseStapling on
SSLStaplingCache "shmcb:logs/stapling-cache(150000)"
SSLSessionTickets Off
# Other security options.
# Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubDomains; preload"
Header always set X-Frame-Options DENY
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options nosniff
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Upgrade} websocket [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Connection} upgrade [NC]
RewriteRule .* "ws://localhost:8443%{REQUEST_URI}" [P]
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto https
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Port 443
ProxyRequests off
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8443/ nocanon
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8443/
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Make sure to set the ProxyPass, ProxyPassReverse and RewriteRule
directives to the actual address of your code-server instance and the
ServerName directive to the hostname of your website. If you're using SSL,
make sure to change the SSLCertificateFile, SSLCertificateKeyFile, and
SSLCertificateChainFile directives. If not, remove the HTTPS IfModule block
entirely.
For more details about Apache reverse proxy configuration, check out the mod_proxy documentation.